
Light Intensity and Duration
0 Comments
/
There are two important factors for providing light to house plants which are intensity and duration. Of course we all know there are varying intensities of light and the term which we use to calculate the intensity are referred to as PAR, photo-synthetically active radiation. Amount of light exposure is based on plant types typically in ranges between 8 to 18 hours. But when working with High intensity LED’s, the nutrient and water intake with certain plant families may be reduced slightly.

Light Saturation Point
Umol or micromole measures the amount of photons (light particles) that cover a specific area over a specific amount of time (per/s or per/day) when you can achieve maximum photons absorb-able by your plant species this is called light saturation point (LSP). Light saturation point is important because this allows your plant to take full advantage of nutrients, use less water and to maximize the C02 intake, provided the temperature and the humidity are at an optimal level.
There are many metric units that are used for different purposes. The most basic way to measure light is in English units called, foot-candle.
0 foot-candle = darkness
100 foot-candles = your livingroom or your kitchen
1000 foot-candles = (June 21st) The longest day of the year at noon, at the equator with zero humidity. An instantaneous foot-candle measurement cannot take day-length into account but foot-candle measurements are certainly better than trying to make estimates of light with your eyes when analyzing light intensities (inside and outside) the growing space or greenhouse when using artificial light such as LED grow lights.
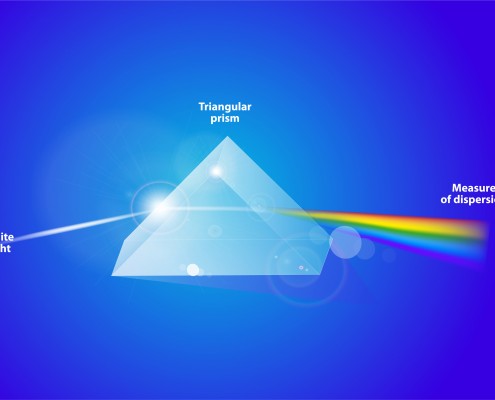
Colour of Light and Energy Levels
Plants get their energy from light, but you might not know that different colors of light have different energy levels. Think about the colors of a rainbow. All of these colors are in white light. While using a prism you can separate the white light into the colors. (That’s what the raindrops are doing when we see a rainbow.) At the purple, violet & blue end of the scale the light is at its highest energy. It has short wavelengths. The red end is lower energy, it has long wavelengths.
What wavelength goes with with a colour?
LED vs HID vs CFL’s
LED's are considered heavy-duty, they have no electrode or filament, and they are shock & vibration resistant. Led's turn on instantly, the do not flicker and they create focused light. LED"s are a higher upfront cost but as compare to that of their predecessor there are virtually no maintenance expenses.
Unlike incandescent bulbs, which use a filament, or compact florescent lamps (CFL's), which rely on gas, LED's create light by exciting electrons. Inside each LED is a semiconductor material consisting of positively and negatively charged parts. When the light is turned on and an electricity strikes the semiconductor, electrons become charged and begin to flow from a negative to a positive layer within the semiconductor.
